Diabetes patients often suffer from non-healing infected wounds, which poses a serious threat to their health and quality of life. Efficient revascularization has been one of the most potential treatments for promoting healing of diabetic wound. However, high glucose microenvironment of diabetic wound commonly induces the massive accumulation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and bacterial infection, further leading to the difficulties of vascular regeneration and slow wound-closure rate in diabetic wound. Hence, a novel strategy for integrated removal of AGEs and anti-bacteria is especially important for diabetic chronic wound healing but also an enormous challenge.
Recently, Professor Chuanliang Feng and Associate Professor Xiaoqiu Dou from Shanghai Jiao Tong University cooperate with Professor Yong Fang and Researcher Yinbo Peng from Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine to develop a novel chiral gel dressing for promoting infected diabetic wound healing. The research results, entitled “Infected Diabetic Wound Regeneration Using Peptide-Modified Chiral Dressing to Target Revascularization”, were published in ACS Nano.
Herein, the chiral gel possesses abundant chiral and cationic sites, not only effectively reducing AGEs via stereoselective interaction, but also specifically killing multidrug resistant bacteria rather than host cells since cationic hexapeptides selectively interact with negatively charged microbial membrane. it is unexpected that the chiral gel dressing exhibits the ability to activate sprouted angiogenesis of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs) by upregulating VEGF and OPA1 expression during healing. In comparison with clinical Prontosan® Wound Gel, the chiral gel dressing presents superior healing efficiency in the infected diabetic wound in the respect of angiogenesis and re-epithelialization, shortening the healing period from 21 days to 14 days.
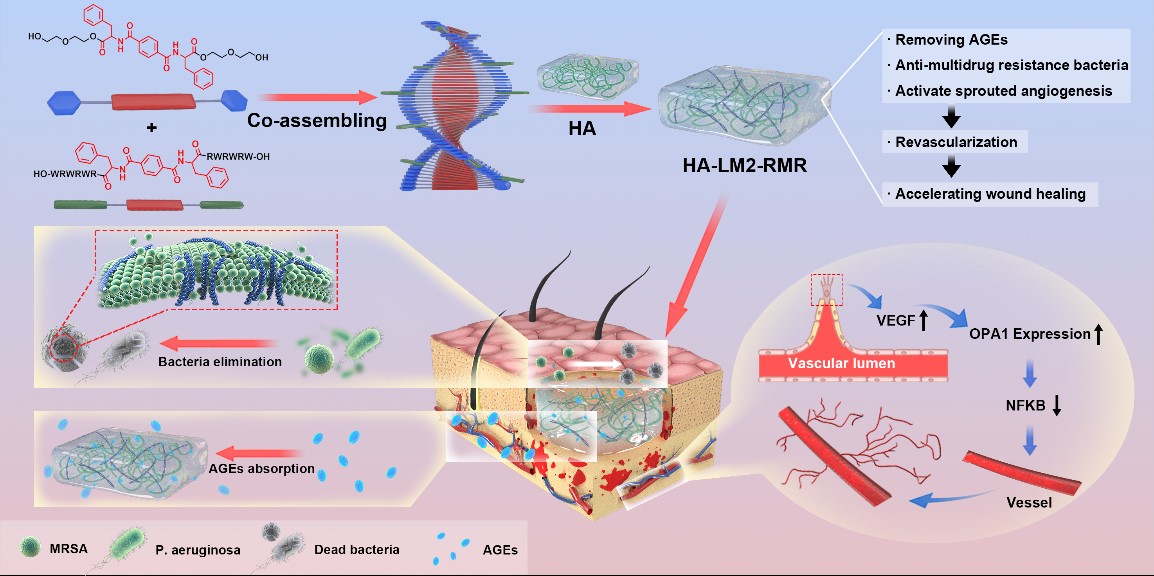
Schematic illustration of the structure of chiral gel dressing and the therapeutic mechanisms in infected diabetic wound.
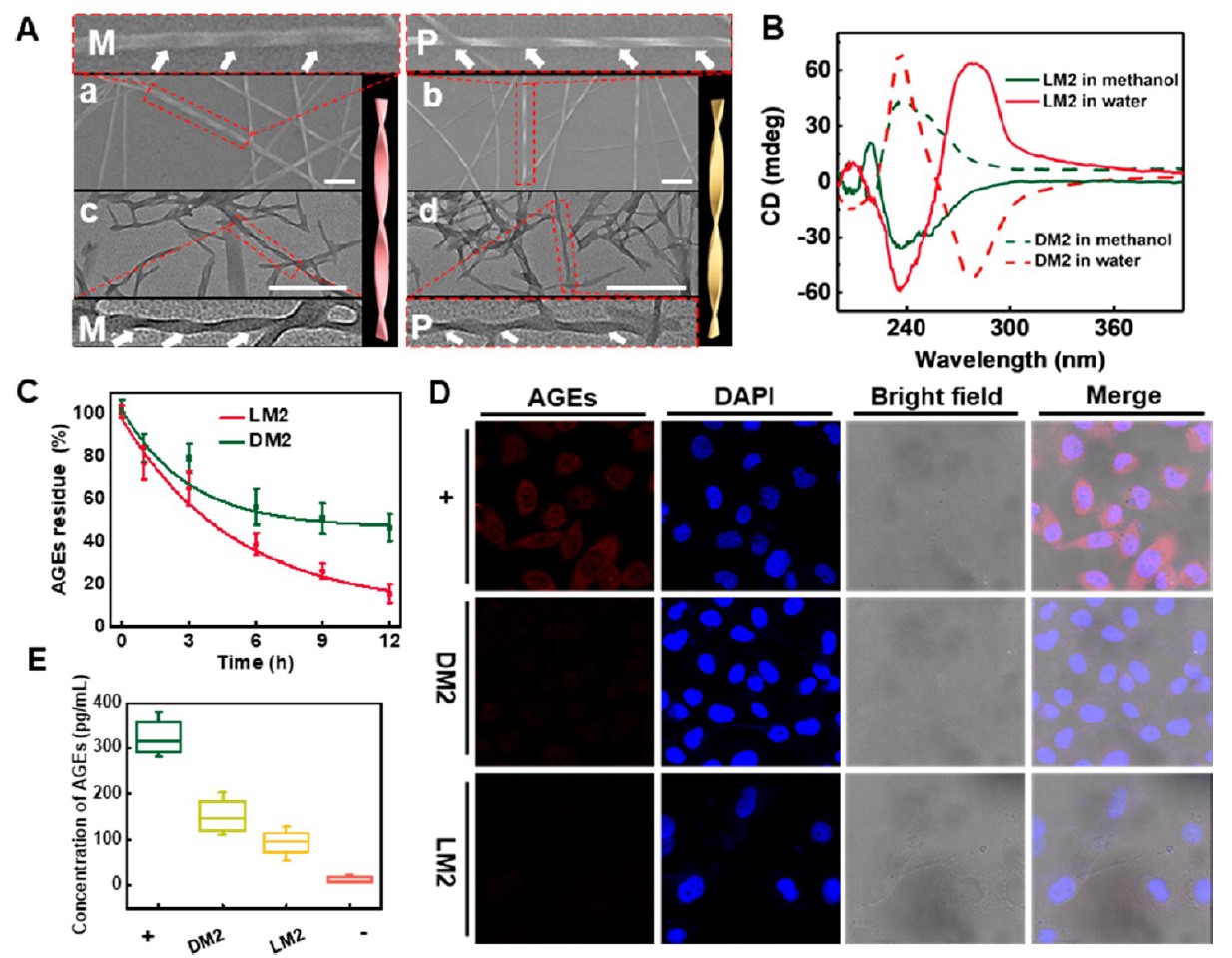
The inner structures of chiral gel dressings and AGEs removal results.
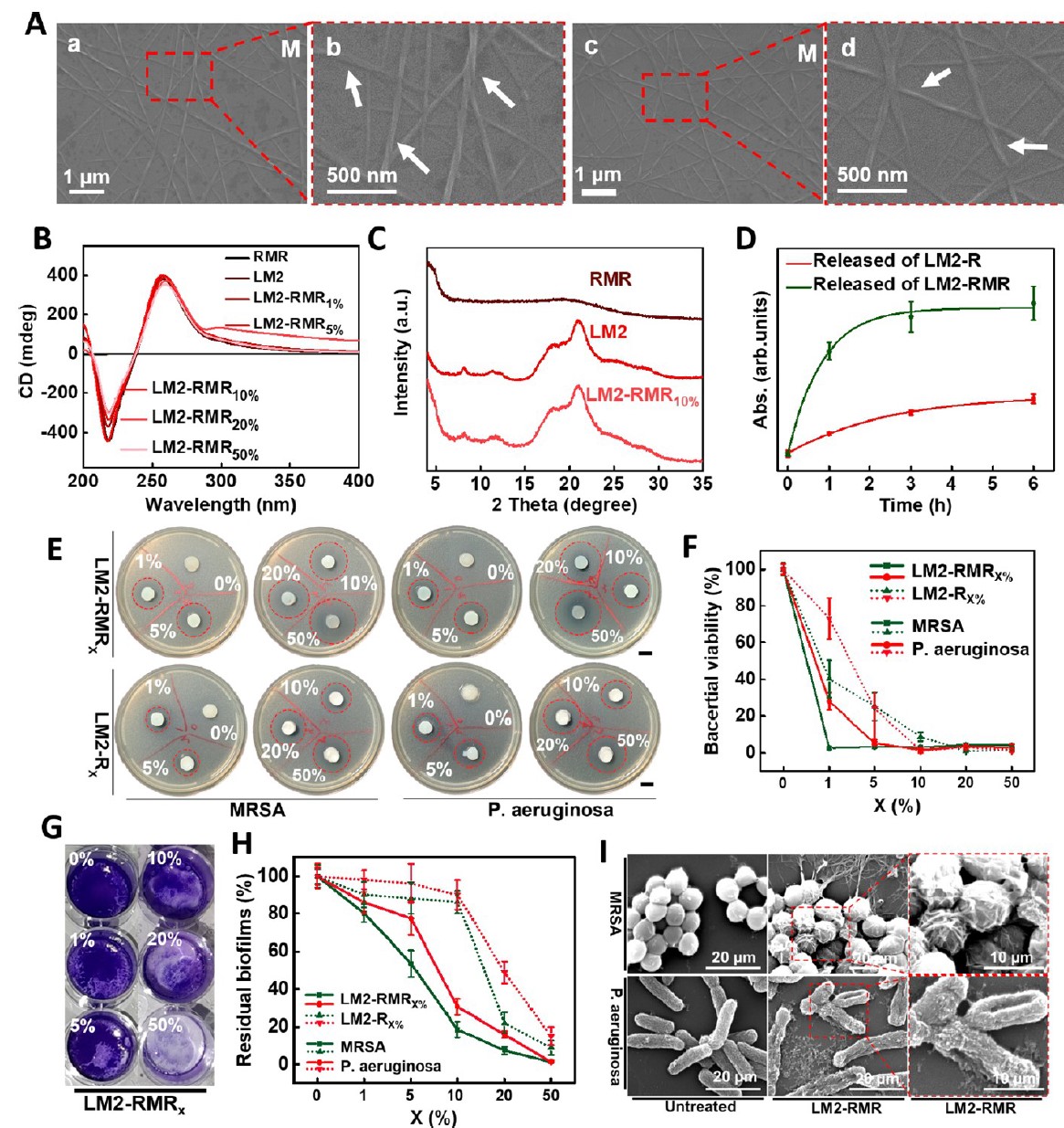
Antimicrobial activity of chiral gel dressings.
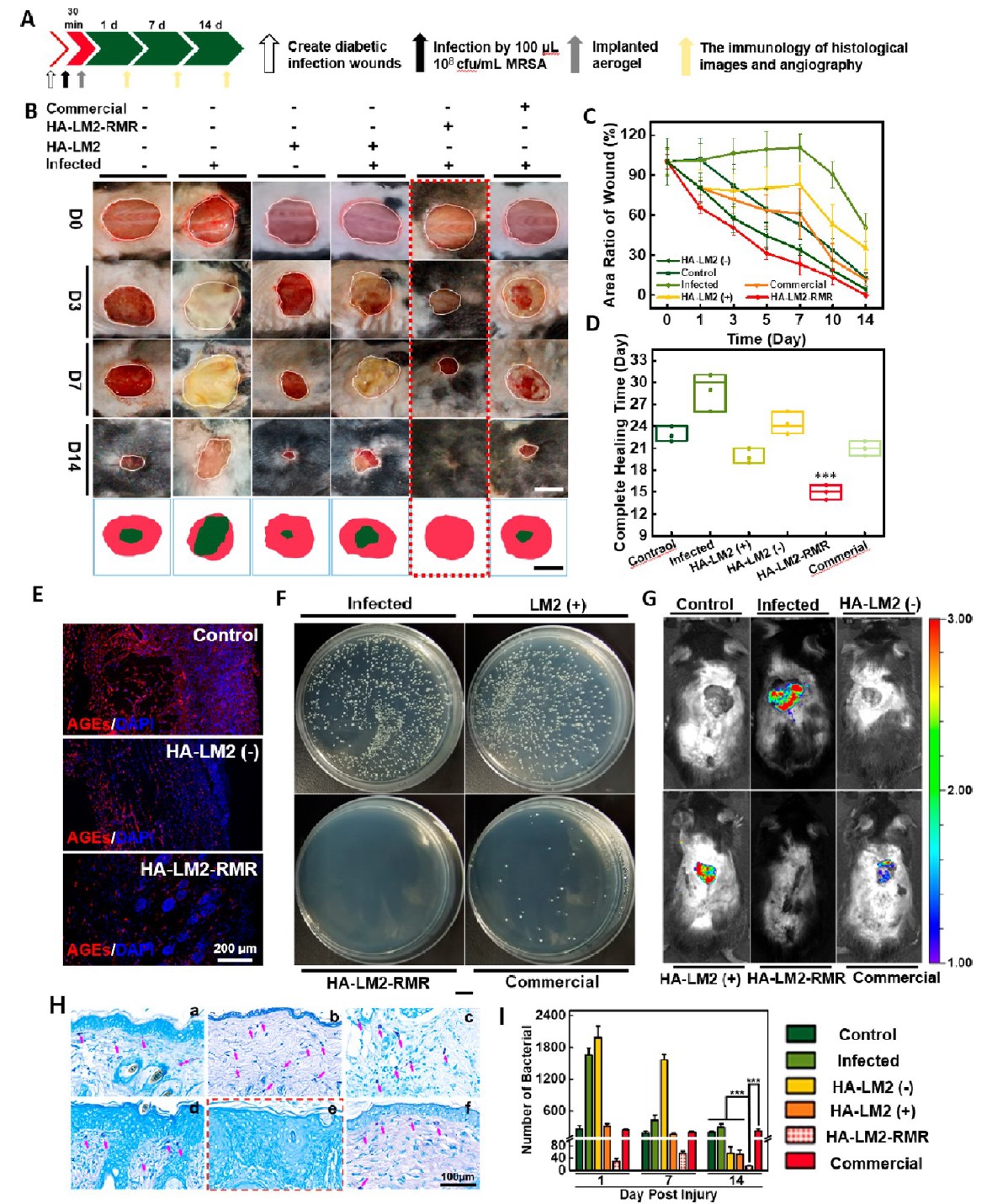
Chiral gel dressing significantly improves infected diabetic wound regeneration in diabetic mice.
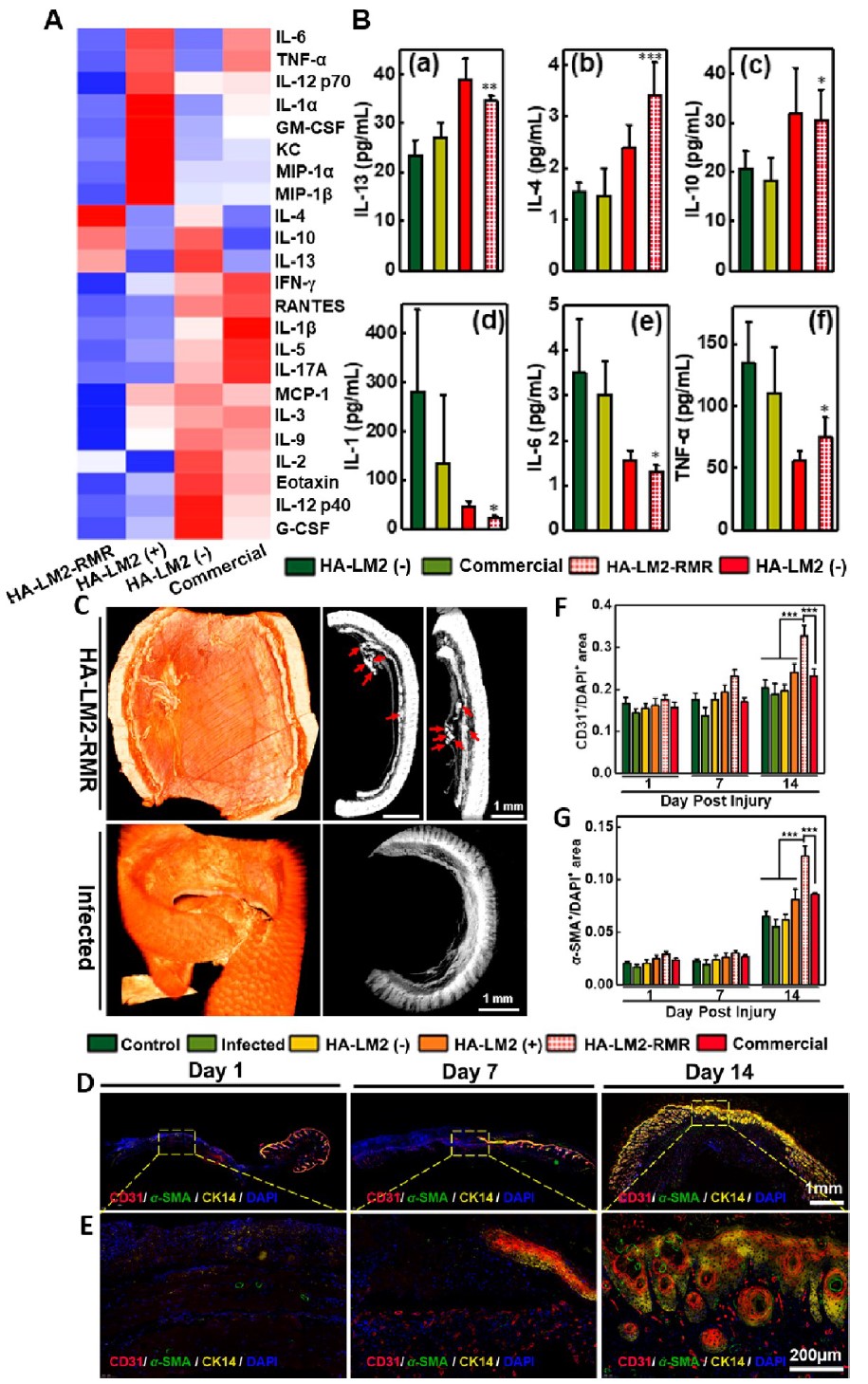
Chiral gel dressing relieves inflammation and promoted vascularization.
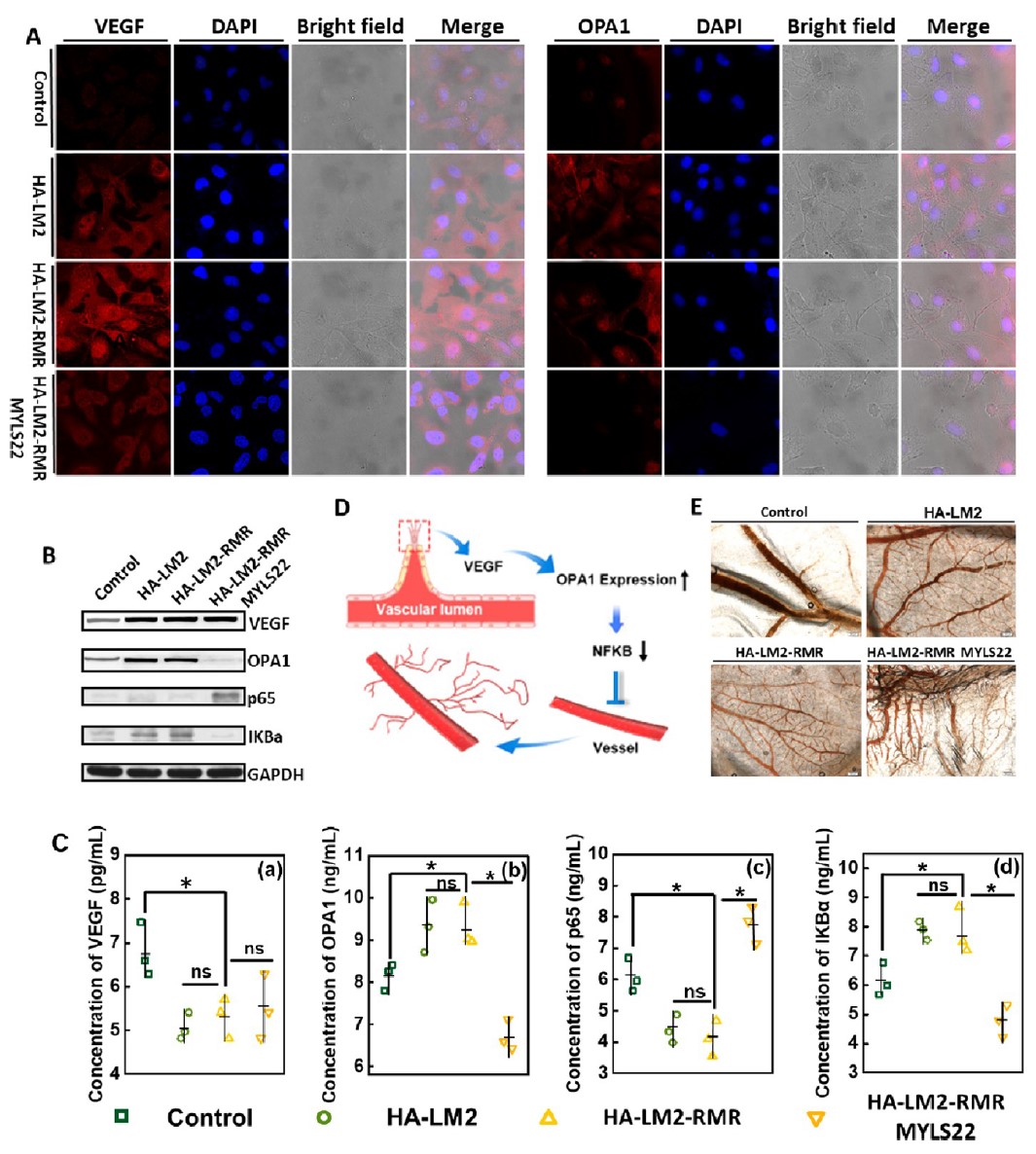
Chiral gel dressing promotes vascularization in vitro.
Owing to the importance of revascularization in the management of diabetic complications, this new chiral biomedical material may find broad utility in the treatment of diabetic complications, such as peripheral neuropathy and peripheral artery diseases. Xing Chao from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Hanting Zhu from Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine are the co-first authors in the manuscript.
